随着辅助生殖技术的发展,玻璃化冷冻已广泛应用于胚胎保存。根据中华医学会生殖医学分会(Chinese society of reproductive medicine,CSRM)数据显示,中国2019年的全胚冷冻率为50.68%[1],冻融胚胎移植(frozen embryo transfer,FET)能够更好地改善胚胎与子宫内膜的同步性。囊胚移植相比较于卵裂期胚胎移植具有更高的种植率,提高妊娠率的同时可以进一步降低多胎妊娠率和母婴并发症的风险[2]。《人类体外受精-胚胎移植实验室操作专家共识(2016)》认为Day 5和Day 6形成的囊胚均可进行移植或冷冻,Day 5的囊胚着床率高于Day 6的囊胚[3]。Bourdon等人[4]的一项Meta分析显示,Day 5囊胚具有比Day 6囊胚更高的临床妊娠率和活产率。因此,在临床实践中,同等质量下的Day 5囊胚通常优先于Day 6囊胚进行移植。然而,囊胚的形态学分级对妊娠结果也至关重要[5],对于Day 5仅存有非优质的囊胚而Day 6存在优质囊胚可用的患者,如何选择仍有争议。为选择合适的胚胎移植策略,帮助患者缩短到达妊娠时间(Time to pregnancy,TTP),本研究回顾性分析本中心1991例冻融周期单囊胚移植患者的周期资料,探究对比Day 5非优质囊胚和Day 6优质囊胚的临床结局,为临床实施单囊胚冻融移植策略提供进一步参考。
对象与方法
一、研究对象
回顾性分析2017年1月1日至2022年6月30日在南京大学医学院附属鼓楼医院生殖医学科行单囊胚FET患者的临床资料,根据患者冷冻囊胚的质量,在FET周期中依次解冻,分为Day 5非优质单囊胚移植组(n=1 083)和Day 6优质单囊胚移植组(n=908)。纳入标准:(1)单囊胚FET周期;(2)女方年龄<40周岁;(3)移植日内膜厚度≥8 mm。排除标准:(1)PGT周期,供卵周期;(2)合并子宫内膜异位症、子宫肌瘤或免疫性不孕等影响胚胎种植的疾病;(3)患有全身系统性疾病的患者等。
二、研究方法
1.胚胎培养与囊胚评估:按照本中心常规促排卵方案及体外受精流程,将Day 3移植或冷冻后的剩余胚胎转移至含有G2的囊胚培养液(Vitrolife,Sweden)中继续培养至Day 5或Day 6。依据Gardner评分标准[6]进行囊胚评估,根据囊胚质量对扩张等级≥4级,内细胞团和滋养层评分不同时为C的囊胚(AA、AB、BA、BB、AC、BC、CA和CB)进行玻璃化冷冻。本中心优质囊胚的定义为扩张等级≥4级,同时内细胞团和滋养层质量均在B级以上者(即AA、AB、BA和BB),非优质囊胚的定义为扩张等级≥4级,囊胚质量为AC、BC、CA和CB。
2.囊胚冷冻与复苏:将待冷冻的囊胚行激光辅助孵化,待囊胚腔皱缩后转移至平衡液ES(KITAZATO,日本)中静置10~12 min后,于玻璃化冷冻液VS(KITAZATO,日本)中充分洗涤后转移至冷冻载杆,载杆前端完全浸入液氮,洗涤至入液氮的操作于60 s内完成。囊胚复苏:将待复苏囊胚依次置于复苏液TS、DS、WS、WS(KITAZATO,日本)中,分别1 min、3 min、5 min、1 min,最后转移至含有G2囊胚培养液(Vitrolife,Sweden)的培养皿中,行激光辅助孵化后于37℃、6%CO2和5%O2的培养箱内培养2 h等待移植。
3.内膜准备及囊胚移植:子宫内膜准备采用人工激素替代周期,即月经第2天开始服用芬吗通(雅培,荷兰)(雌二醇片,2 mg,每日3次),12至14 d后进行血清雌孕激素检测以及阴道超声检查,若子宫内膜厚度<8 mm,芬吗通增量至8 mg/d,4至6 d后复查,子宫内膜≥ 8 mm且血清孕激素水平<1 ng/mL时,开始改为服用芬吗通(雌二醇/地屈孕酮片,2 mg/10 mg,每日3次),同时黄体酮注射液(浙江仙琚)60 mg/d肌肉注射进行子宫内膜转化,第6日进行囊胚解冻移植。移植后继续服用芬吗通(雌二醇/地屈孕酮片,2 mg/10 mg,每日3次)联合黄体酮凝胶(默克雪兰诺,瑞士)阴道用药(90 mg,每日1次)进行常规雌孕激素支持。4~6周后超声下见妊娠囊为临床妊娠,并于孕早晚期、分娩时、分娩后两个月内对围产期结局相关指标进行随访(包括流产率、单卵双胎率、活产率、早产率、孕周、新生儿性别比、身长、体重等)。
三、统计学方法
采用SPSS 25.0进行数据分析统计。计量资料均符合正态分布,采用均值 ± 标准差![]() 表示,两组间比较采用t检验;计数资料用率或构成比(%)表示,两组间比较采用卡方检验;多因素分析采用二分类Logistic回归模型分析。P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
表示,两组间比较采用t检验;计数资料用率或构成比(%)表示,两组间比较采用卡方检验;多因素分析采用二分类Logistic回归模型分析。P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
结 果
一、两组患者一般情况比较
共有1 991例FET周期患者纳入统计,根据移植时期和胚胎质量分为Day 5非优质囊胚组(n=1 083)和Day 6优质囊胚组(n=908),两组患者的一般资料均无统计学差异。见表1。
表1 两组患者一般情况比较![]() 例(%)]
例(%)]
Table 1 Comparison of Baseline Characteristics Between the Two Groups ![]()
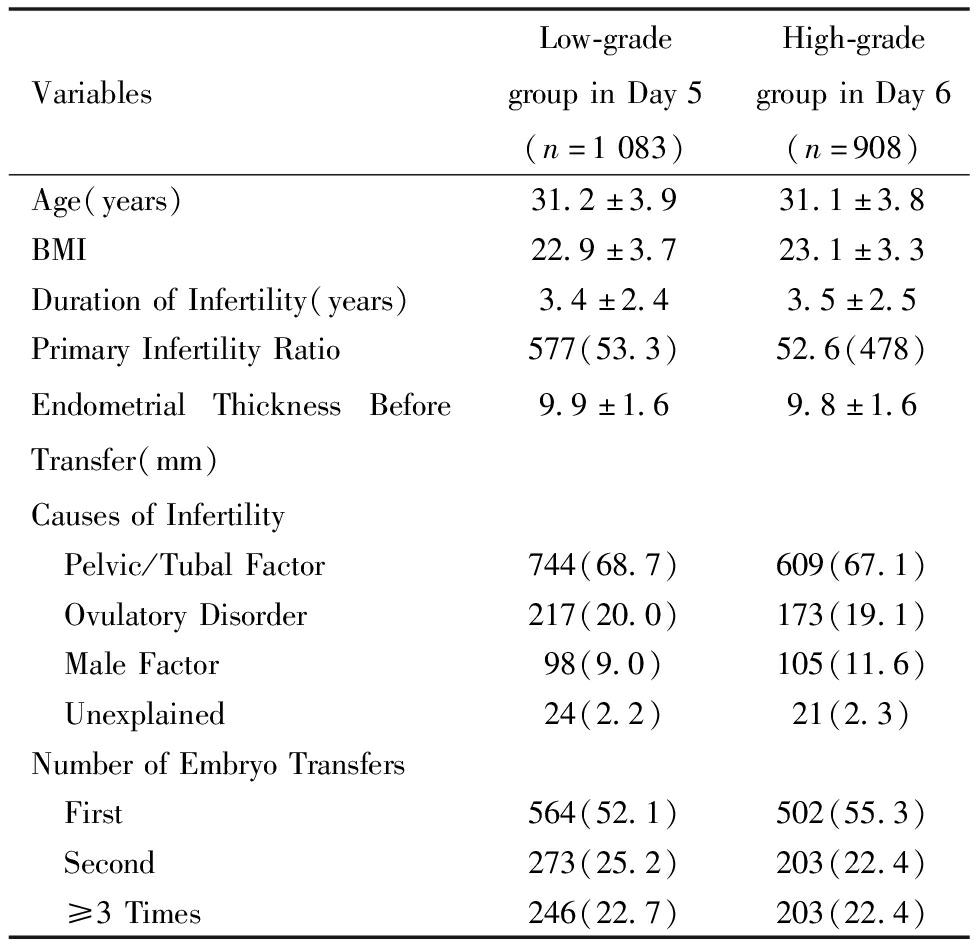
VariablesLow-gradegroupinDay5(n=1083)High-gradegroupinDay6(n=908)Age(years)31.2±3.931.1±3.8BMI22.9±3.723.1±3.3DurationofInfertility(years)3.4±2.43.5±2.5PrimaryInfertilityRatio577(53.3)52.6(478)EndometrialThicknessBeforeTransfer(mm)9.9±1.69.8±1.6CausesofInfertility Pelvic/TubalFactor744(68.7)609(67.1) OvulatoryDisorder217(20.0)173(19.1) MaleFactor98(9.0)105(11.6) Unexplained24(2.2)21(2.3)NumberofEmbryoTransfers First564(52.1)502(55.3) Second273(25.2)203(22.4) ≥3Times246(22.7)203(22.4)
二、两组患者的临床妊娠及围产期结局比较
两组患者的临床妊娠率、异位妊娠率、流产率、单卵双胎率、活产率、早产率、新生儿体重均无统计学差异,但Day 5非优质囊胚组的出生男婴比例显著低于Day 6优质囊胚组(1.1与1.5,P <0.05)。见表2。
表2 两组患者的临床妊娠及围产期结局比较![]()
Table 2 Comparison of Clinical Pregnancy and Perinatal Outcomes Between Groups![]()
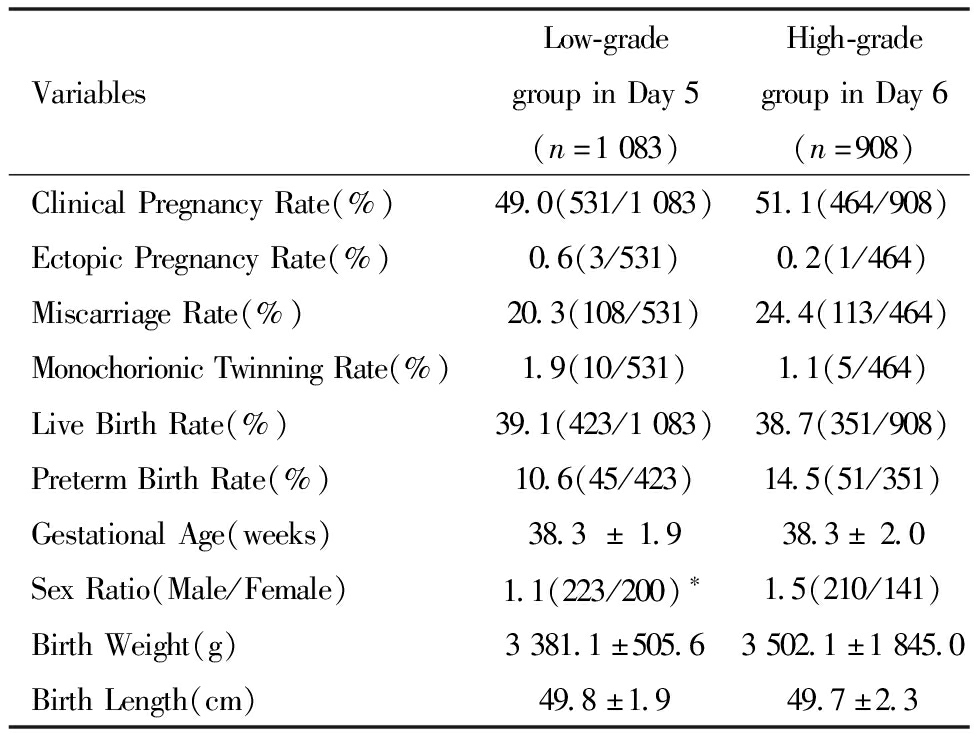
VariablesLow-gradegroupinDay5(n=1083)High-gradegroupinDay6(n=908)ClinicalPregnancyRate(%)49.0(531/1083)51.1(464/908)EctopicPregnancyRate(%)0.6(3/531)0.2(1/464)MiscarriageRate(%)20.3(108/531)24.4(113/464)MonochorionicTwinningRate(%)1.9(10/531)1.1(5/464)LiveBirthRate(%)39.1(423/1083)38.7(351/908)PretermBirthRate(%)10.6(45/423)14.5(51/351)GestationalAge(weeks)38.3±1.938.3±2.0SexRatio(Male/Female)1.1(223/200)∗1.5(210/141)BirthWeight(g)3381.1±505.63502.1±1845.0BirthLength(cm)49.8±1.949.7±2.3
Note:Compared with Day 6 high-quality blastocyst group,*P<0.05
三、影响FET临床妊娠率的多因素分析
经Logistic多重回归分析,女方年龄对FET的临床妊娠率有显著影响(P <0.05)。女方BMI、不孕年限、移植日子宫内膜厚度、胚胎移植时期对FET的临床妊娠率均无显著影响(P >0.05)。见表3。
表3 影响FET临床妊娠率的多因素分析
Table 3 Multivariate Analysis of Factors Affecting Clinical Pregnancy Rate in FET
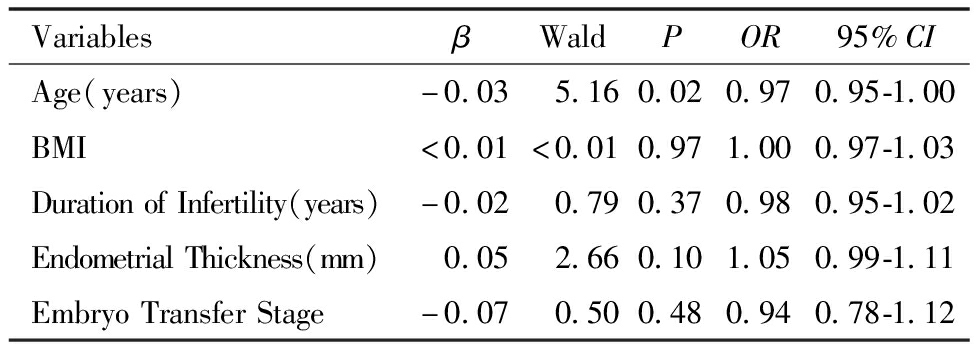
VariablesβWaldPOR95%CIAge(years)-0.03 5.160.020.970.95-1.00BMI<0.01<0.010.971.000.97-1.03DurationofInfertility(years)-0.02 0.790.370.980.95-1.02EndometrialThickness(mm) 0.05 2.660.101.050.99-1.11EmbryoTransferStage-0.07 0.500.480.940.78-1.12
四、年龄分组后的临床结局比较
女方年龄<35岁的患者Day 5非优质囊胚组的流产率显著低于Day 6优质囊胚组,其余指标无统计学差异。见表4。
表4 年龄分组后的临床结局比较(%)
Table 4 Comparison of Clinical Outcomes by Age(%)
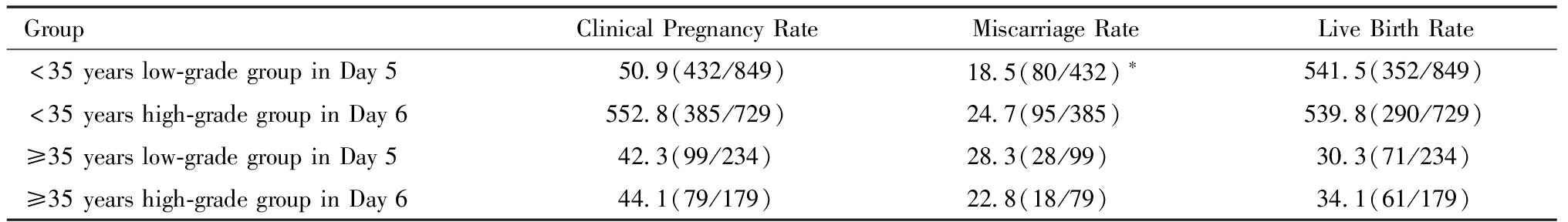
GroupClinicalPregnancyRateMiscarriageRateLiveBirthRate<35yearslow-gradegroupinDay550.9(432/849)18.5(80/432)∗541.5(352/849)<35yearshigh-gradegroupinDay6552.8(385/729)24.7(95/385)539.8(290/729)≥35yearslow-gradegroupinDay542.3(99/234)28.3(28/99)30.3(71/234)≥35yearshigh-gradegroupinDay644.1(79/179)22.8(18/79)34.1(61/179)
Note:Comparedto <35-year-old high-quality blastocyst group in Day 6,*P<0.05
讨 论
随着玻璃化冷冻和单囊胚移植技术的普及,选择具有更高植入潜力的胚胎至关重要。多项研究结果表明,在FET周期中移植同等质量的囊胚,Day 5的囊胚通常比Day 6获得更好的临床结局,同时优质囊胚的妊娠结局明显高于非优质囊胚[4-5]。在FET的临床实践中,对于Day 5仅存有非优质囊胚而Day 6存在优质囊胚可用的患者,如何进行胚胎的选择尚无定论。本研究结果提示移植Day 5非优质囊胚和Day 6优质囊胚的临床结局相似,但移植Day 6优质囊胚可能会造成性别比偏倚的风险,并且对于年龄<35岁的人群,Day 6优质囊胚组的流产率显著高于Day 5非优质囊胚组。
出生性别比(secondary sex ratio,SSR)一般定义为活产男婴与女婴的比值,常用于指示人口健康和生育率的指标。本研究结果显示,移植Day 6优质囊胚会显著增加出生男婴的比例。这与Lou等人的研究结果一致[7],移植高质量囊胚的性别比明显高于低质量的囊胚(60%与49.7%,P<0.01)。Ebner等人[8]的研究认为这种性别比的失衡可能与滋养层细胞的分级有关,出生后为男婴的囊胚获得滋养层质量评分为A的几率是出生后为女婴囊胚的2.53倍。Mao等人[9]认为这可能是由于男性囊胚比女性囊胚滋养层细胞(TE)数目更多,形态学评分更好,并且由于TE分化产生胎盘部分,因此与男性囊胚相比,女性囊胚发生滋养层功能异常的概率可能更高,导致植入和进一步发育的潜力降低。
年龄是影响FET妊娠结局的重要指标,本研究同样提示,年龄是影响FET妊娠结局的独立危险因素,在对年龄分层分析后发现,对于较年轻的患者,Day 6移植会显著增加流产率,这可能与Day 6囊胚的整倍体率较低有关。Tong等人对行胚胎植入前遗传学测试(PGT)的2 531枚囊胚的研究显示[10],Day 5囊胚的整倍体率显著高于Day 6囊胚,但是对于≥38岁的高龄患者,因为延长体外培养时间而导致的整倍体率的差异并不明显,这可能与高龄女性卵子质量下降有关。He等人[11]的研究结果发现,对于高龄的患者Day 5非优质囊胚临床妊娠率显著高于Day 6优质囊胚(46.1%与33.2%,P<0.05),因此对于高龄患者仍然推荐移植Day 5的非优质囊胚。
Bourdon等人[4]的一项Meta分析显示,Day 5囊胚具有比Day 6囊胚更高的临床妊娠率和活产率。Ferreux等人的研究[12]发现优质Day 6囊胚的活产率为18.7%,低于Day 5非优质囊胚的23.5%。据报道,发育进程较慢的胚胎与染色体异常有关,这可能是造成Day 6优质囊胚的活产率低于Day 5非优质囊胚的原因。一项研究结果发现,Day 5囊胚中线粒体DNA(mtDNA)的含量明显高于Day 6的囊胚,而mtDNA的含量可能是影响囊胚发育速率的一个关键因素[13]。此外,Hashimoto等人[14]发现,在对533枚解冻后的Day 5和Day 6囊胚中进行纺锤体分析,Day 6囊胚中异常纺锤体的发生率显著高于Day 5囊胚(47%与30%,P<0.05),与Day 5囊胚相比,Day6囊胚的植入能力降低。然而Shi等人[15]的研究结果却有相反的结论:与非优质的Day 5囊胚相比,优质的Day 6囊胚移植获得了更高的活产,并且与优质的Day 5囊胚移植结果相似。其研究结果认为囊胚的形态学分级对整倍体率的影响可能更大,优质Day 6囊胚的整倍体率高于非优质的Day 5囊胚(54.6%与41.4%),这种差异可能与其纳入的人群和样本量差异有关。
综上所述,在FET周期中Day 5非优质单囊胚移植和Day 6优质单囊胚移植的临床结局相似,但Day 6优质单囊胚移植可能会存在新生儿性别比偏倚的风险,并且对于较年轻的患者,移植Day 6囊胚可能会导致流产率的增加。因此,在Day 5非优质囊胚和Day 6优质囊胚中建议优先选择Day 5非优质囊胚,可能获得更好的临床结局。
1 张孝东,邓成艳,黄学锋,等.中华医学会生殖医学分会:2019年辅助生殖技术数据报告.生殖医学杂志,2022,31:1015-1021.
2 Nagy ZP,Shapiro D,Chang CC.Vitrification of the human embryo:a more efficient and safer in vitro fertilization treatment.Fertil Steril,2020,113:241-247.
3 中华医学会生殖医学分会第一届实验室学组.人类体外受精-胚胎移植实验室操作专家共识(2016).生殖医学杂志,2017,26:1-8.
4 Bourdon M,Pocate-Cheriet K,Finet de Bantel A,et al.Day 5 versus Day 6 blastocyst transfers:a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical outcomes.Hum Reprod,2019,34:1948-1964.
5 Guo N,Deng T,Jiang H,et al.Association between blastocyst morphology and live birth rate following frozen-thawed single blastocyst transfer:Results from a 5-year retrospective analysis of 2593 cryopreserved blastocysts.J Obstet Gynaecol Res,2020,46:2314-2322.
6 Gardner DK,Lane M,Stevens J,et al.Reprint of:Blastocyst score affects implantation and pregnancy outcome:towards a single blastocyst transfer.Fertil Steril,2019,112:e81-e84.
7 Lou H,Li N,Zhang X,et al.Does the sex ratio of singleton births after frozen single blastocyst transfer differ in relation to blastocyst development.Reprod Biol Endocrinol,2020,18:72.
8 Ebner T,Tritscher K,Mayer RB,et al.Quantitative and qualitative trophectoderm grading allows for prediction of live birth and gender.J Assist Reprod Genet,2016,33:49-57.
9 Mao Y,Zeng M,Meng YM,et al.Effect of blastocyst quality on human sex ratio at birth in a single blastocyst frozen thawed embryo transfer cycle.Gynecol Endocrinol,2023,39:2216787.
10 Tong J,Niu Y,Wan A,et al.Comparison of day 5 blastocyst with day 6 blastocyst:Evidence from NGS-based PGT-A results.J Assist Reprod Genet,2022,39:369-377.
11 He Y,Tang Y,Liu H,et al.No advantage of single day 6 good-quality blastocyst transfer versus single day 5 poor-quality blastocyst transfer in frozen-thawed cycles stratified by age:a retrospective study.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth,2023,23:79.
12 Ferreux L,Bourdon M,Sallem A,et al.Live birth rate following frozen-thawed blastocyst transfer is higher with blastocysts expanded on Day 5 than on Day 6.Hum Reprod,2018,33:390-398.
13 Wu FS,Weng SP,Shen MS,et al.Suboptimal trophectoderm mitochondrial DNA level is associated with delayed blastocyst development.J Assist Reprod Genet,2021,38:587-594.
14 Hashimoto S,Amo A,Hama S,et al.Growth retardation in human blastocysts increases the incidence of abnormal spindles and decreases implantation potential after vitrification.Hum Reprod,2013,28:1528-1535.
15 Shi W,Zhou H,Chen L,et al.Live birth rate following frozen-thawed blastocyst transfer is higher in high-grade day 6 blastocysts than in low-grade day 5 blastocysts.Front Endocrinol(Lausanne),2022,13:1066757.