上皮性卵巢癌(epithelial ovarian cancer,EOC)是女性生殖系统常见的恶性肿瘤之一。卵巢癌易于复发和转移,具有很高的死亡率[1]。胸苷酸合成酶(thymidylate synthetase, TYMS)是一种参与DNA复制和修复的酶[2]。目前有研究报道,TYMS在乳腺癌、肺癌、肝癌和前列腺癌中高表达且与不良临床结果相关[3-6],但未见TYMS在卵巢癌中的研究报道。本研究以生物信息学分析为基础,对EOC中TYMS的表达及其相关基因的生物学功能、信号通路进行分析。
资料与方法
一、资料
1.Oncomine数据库(https://www.oncomine.org/)是目前世界上最大的癌基因芯片数据库和整合数据挖掘平台[7]。
2.cBioPortal数据库(https://www.cbioportal.org/)是一个用于探索分析和可视化多维癌症基因组学和临床数据的开放源代码平台[8]。
3.STRING数据库(https://string-db.org/;version 11.0)是一个可用于预测和跟踪蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用的网络[9]。
4.DAVID软件(https://david.ncifcrf.gov/home.jsp; version 6.8)是一个集成了生物数据,用于注释,可视化和集成发现的数据库[10]。GO分析阐明与基因相关的潜在生物过程(BP),分子功能(MF)和细胞成分(CC)。KEGG整合了大量由高通量实验技术产生的实用数据库资源。
5.Sangerbox(http://www.sangerbox.com/tool)工具是一个免费的在线数据分析平台。
二、方法
1.Oncomine数据库分析TYMS表达情况:本研究应用Oncomine 平台分析TYMS在卵巢癌和正常卵巢样本中的表达情况,输入TYMS基因并设置为“ovarian cancer、mRNA或DNA、Differential Analysis Cancer vs.Normal Analysis”进行表达分析,其阈值为P值<0.05。
2.cBioPortal数据库挖掘TYMS相关基因:本研究中cBioPortal用于挖掘TYMS在卵巢癌中的相关基因,选择用于可视化和分析的研究,并设置为“Ovarian Serous Cystadenocarcinoma(TCGA, Nature 2011)、TYMS”,点击“Network”,查看与TYMS基因关系密切的基因调控网络图,共有39个基因。
3.STRING数据库构建TYMS相关基因的PPI网络:本研究使用STRING构建TYMS及相关基因的PPI网络,将TYMS及其相关基因导入“Multiple proteins”中,并设置为“Homo sapiens”,其阈值为交互关系置信度>0.4,获取图表。
4.DAVID软件探究TYMS及相关基因生物学功能和通路:本研究使用DAVID软件完成GO分析和 KEGG 通路分析。将TYMS及相关基因导入DAVID中,并设置为“OFFICIAL_GENE_SYMBOL、Homo sapiens”,选择“GOTERM_BP_DIRECT、GOTERM_CC_DIRECT、GOTERM_MF_DIRECT、KEGG_PATHWAY”进行富集分析,其阈值为P值<0.05,FDR<0.5。最后,富集分析结果通过Sangerbox 工具可视化。
结 果
一、Oncomine数据库中TYMS在卵巢癌中的表达
Oncomine 数据库关于卵巢癌中TYMS基因差异表达的研究文献共13项,包括1043例标本。文章分别发表于国际Br J Cancer,Cancer Res,Clin Cancer Res,Cancer Sci等杂志,在Oncomine数据中对这13项研究结果进行统计分析发现,TYMS在卵巢癌中呈现高表达,且差异具有统计学意义,见图1。
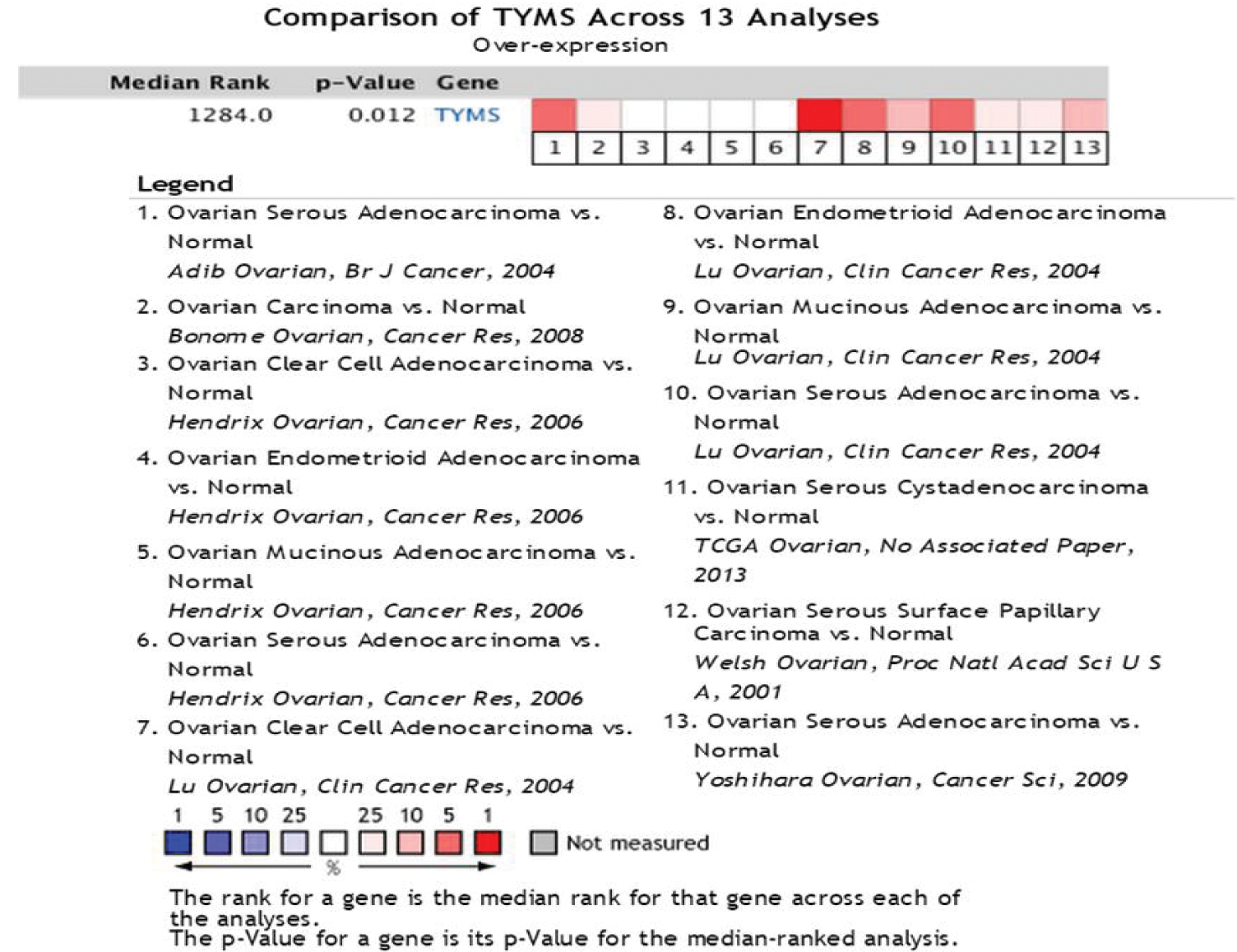
图1 Oncomine数据库中TYMS在卵巢癌中的表达
Figure 1 The expression of TYMS in the ovarian cancer from Oncomine database
二、TYMS相关基因识别与PPI网络构建
在cBioPortal数据库中,卵巢癌中与TYMS密切相关的基因共39个,分别为ATIC、CCNA1、CCNE1、CDC45A、CDC45、CDC6、CDT1、CSNK2A1、CSNK2A2、DHFR、DHFR2、E2F1、E2F3、FBXO5、GART、MTR、MTRR、ORC1、PCNA、POLA1、POLA2、POLD1、POLD2、POLD3、POLD4、POLE、POLE2、POLE3、POLE4、POLG、POLG2、PRIM1、PRIM2、REV3L、RRM2、SLC25A32、TFDP2、TK1、TK2。STRING构建包括TYMS基因在内的40个基因的PPI网络,图中可直观显示各相关基因与TYMS的相互作用,见图2。

图2 卵巢癌中TYMS相关基因的蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用网络
Figure 2 Protein-protein interaction network of TYMS-related genes in the ovarian cancer
三、TYMS及相关基因的功能富集分析
在DAVID中对TYMS及其相关基因进行GO功能和KEGG途径富集分析。GO功能注释显示了丰富的生物过程,由BP、CC和MF组成。GO分析结果显示,TYMS及其相关基因分别于BP中的细胞周期G1/S调控、DNA生物合成、氨基酸生物合成、DNA代谢、辅酶代谢、核苷酸的生物合成等过程有关;与CC中的核染色体、DNA聚合酶复合物和线粒体等细胞组分有关;与MF中的DNA结合、DNA聚合酶活性和核苷酸结合等分子功能有关。KEGG途径富集分析显示,TYMS及其相关基因包括嘧啶代谢、DNA复制、嘌呤代谢等代谢途径,p53、NF-κB、Wnt、AMPK等信号通路,膀胱癌、前列腺癌、黑色素瘤、非小细胞肺癌、急性髓系白血病等恶性肿瘤,以及细胞周期、叶酸一碳池、铂耐药、HTLV-I感染等在内的58条KEGG通路,见图3。

(A-C):GO terms of the top 39 genes positively correlated with TYMS, including biological processes(BP), molecular function(MF), and cellular component(CC);(D):KEGG pathway of the top 39 genes positively correlated with TYMS
图3 卵巢癌中TYMS的功能和途径富集分析
Figure 3 Enrichment analysis of functions and pathways of TYMS in the ovarian cancer
四、挖掘TYMS上游调控基因E2F3
结合TYMS相关基因的GO功能和KEGG通路富集分析结果,发现TYMS基因的主要生物学功能包括调节细胞周期、细胞分化、细胞周期转化、蛋白质合成等,其中调节有丝分裂细胞G1/S期转化为排在第一位的细胞生物学功能,富集分析提示TFDP2、CCNE1、E1F1、E2F3为G1/S期转化中的上调基因,见图4,提示TFDP2、CCNE1、E1F1、E2F3可能为TYMS的上调基因,值得进一步研究。

图4 细胞周期通路图(红框为富集分析上调基因)
Figure 4 Diagram of the cell cycle pathway(The red frame shows the up-regulated genes for enrichment analysis)
讨 论
TYMS在胸苷单磷酸(deoxy-thymidine monophosphate, dTMP)的生物合成中起关键作用。TYMS是一种74 kda蛋白,它形成一种同型二聚体,利用辅助因子ch2h4-叶酸催化脱氧尿苷一磷酸(deoxy-uridine monophosphate, dUMP)的还原甲基化生成dTMP。dTMP是DNA合成的基本底物。所以,抑制TYMS的表达会导致核苷酸失衡,进而导致细胞死亡[11],TYMS高表达可促进癌变[12],导致恶性肿瘤的发生[13]。
本研究通过Oncomine数据库发现,TYMS在EOC癌组织中表达显著高于正常卵巢组织中的表达,与其他学者在其他恶性肿瘤如乳腺癌、肺癌、肝癌和前列腺癌[3-6]等的研究报道一致。这一结果提示,TYMS高蛋白表达水平与EOC发生关系密切,在EOC的发生中可能扮演癌基因的作用。
为进一步探讨TYMS在EOC中可能的作用机理。本研究通过cBioPortal数据库,获得了EOC中与TYMS表达呈正相关的基因共39个,并在STRING数据库中构建了TYMS相关基因的PPI网络。通过DAVID数据库进行GO功能和KEGG通路富集分析,本研究发现,TYMS的主要生物学功能为调节有丝分裂细胞G1/S期转化、细胞周期、DNA生物合成、氨基酸生物合成、DNA代谢等,提示TYMS可能通过调节有丝分裂细胞G1/S期转化、细胞周期、嘧啶代谢、DNA复制和碱基切除修复等通路,参与EOC的发生发展。
为了探讨TYMS在EOC中高表达的原因,本研究还发现转录因子Dp-2(transcription factor dp-2, TFDP2)、细胞周期蛋白E1(cyclin e1, CCNE1)、E1F转录因子1(E1F transcription factor 1, E1F1)、E2F转录因子3(E2F transcription factor 3, E2F3)可能为TYMS的上调基因。首先,TFDP基因编码一个转录因子家族,与E2F家族蛋白形成的E2F-TFDP转录因子异源二聚体是细胞周期S期进展所需基因的主要调节因子[14]。TFDP2或TFDP家族的其他成员可能通过与E2F家族成员合作来激活下游基因TYMS、CCNE1。例如,已有研究证实,在肝细胞癌中TYMS、CCNE1的表达水平与TFDP1和E2F1密切相关[15]。其次,CCNE1基因在G1/S过渡期间表达,编码属于高度保守的细胞周期蛋白家族。研究表明,晚期 SV40 因子(late SV40 factor 3, LSF)是从静止进展到细胞周期所必需的一种转录因子,并在G(1)/S周期调节TYMS基因的表达,而LSF主要被CCNE家族磷酸化[16]。所以,CCNE1或CCNE家族的其他成员可能通过间接作用调节TYMS基因的表达来产生下游效应。最后,转录因子E2F控制TYMS的表达[17-18],存在于机体大多数细胞中,参与细胞周期进展、细胞增殖、分化和凋亡等生理过程。核转录因子E2F3是一种细胞周期关键蛋白,也是调控细胞有丝分裂的重要因子,调节细胞周期的进展[19],与多种致癌、抑癌基因密切相关。国内外多位学者对E2F3基因促进EOC进展的机制进行了研究。例如,Reimer等[20]的研究发现,E2F3在EOC进展中受表皮生长因子影响,在肿瘤细胞增殖中起着关键作用。He等[21]的研究发现在 EOC 细胞周期中,E2F3与极光家族丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶-A蛋白(Aurora family of serine/threonine protein kinases-A,Aurora-A)的启动子结合,形成E2F3-Aurora-A轴,E2F3异位表达刺激启动子活性,诱导Aurora-A表达增加,促进癌细胞G2/M细胞周期进展。
综上所述,本研究利用生物信息技术在公共肿瘤数据库中进行目标基因的分析,发现TYMS基因在EOC中表达显著增高,并通过调节有丝分裂细胞G1/S期转化、细胞周期、嘧啶代谢、DNA复制和碱基切除修复等通路,参与EOC的发生发展。其次,E2F3可能通过与TYMS结合调控其表达,调节细胞周期进展,促进EOC进展。本研究是一项初步研究,在未来需要进一步的体内和体外实验来验证TYMS的生物学功能,揭示TYMS在卵巢癌的发病机制,探索TYMS作为EOC诊断、预后预测及靶向治疗的潜在生物标志物的研究价值。生物信息学作为一种新兴的科学,对生物医学的研究中寻找关键基因及潜在的治疗靶点具有重要意义,省时、省力,并可减少盲目性。
1 Webb PM,Jordan SJ.Epidemiology of epithelial ovarian cancer.Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol,2017,41:3-14.
2 Gallegos-Arreola MP,Zuniga-Gonzalez GM,SanchezLopez JY,et al.TYMS 2R3R polymorphism and DPYD[IVS]14+1G>A gene mutation in Mexican colorectal cancer patients.Acta Biochim Pol,2018,65:227-234.
3 Donner DB,Nakakura EK,Venook AP,et al.High thymidylate synthase gene expression predicts poor outcome after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma.PLoS One,2019,14:e0219469.
4 Gupta P,Suman S,MishraM,et al.Autoantibodies against TYMS and PDLIM1 proteins detected as circulatory signatures in Indian breast cancer patients.Proteomics Clin Appl,2016,10:564-573.
5 Russo GI,Bier S,Hennenlotter J,et al.Expression of tumour progression-associated genes in circulatingtumour cells of patients at different stages of prostate cancer.BJU Int,2018,122:152-159.
6 Sun S,Shi W,WuZ,et al.Prognostic significance of the mRNA expression of ERCC1,RRM1,TUBB3 and TYMS genes in patients with non-small cell lung cancer.Exp Ther Med,2015,10:937-941.
7 Rhodes DR,Kalyana-Sundaram S,Mahavisno V,et al.Oncomine 3.0:Genes,Pathways,and Networks in a Collection of 18,000 Cancer Gene Expression Profiles.Neoplasia,2007,9:166-180.
8 Wu P,Heins ZJ,Muller JT,et al.Integration and Analysis of CPTAC Proteomics Data in the Context of Cancer Genomics in the cBioPortal.Mol Cell Proteomic,2019,18:1893-1898.
9 Szklarczyk D,Gable AL,Lyon D,et al.STRING v11:protein-protein association networks with increased coverage,supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets.Nucleic Acids Res,2019,47:D607-D613.
10 Huang DW,Sherman BT,Tan Q,et al.The DAVID Gene Functional Classification Tool:A novel biological module-centric algorithm to functionally analyze large gene lists.Genome Biol,2007,8:1-16.
11 Hamzic S,Kummer D,Froehlich TK,et al.Evaluating the role of ENOSF1 and TYMS variants as predictors in fluoropyrimidine-related toxicities:An IPD meta-analysis.Pharmacol Res,2020,152:104594.
12 Bertino JR,Banerjee D.Thymidylate synthase as an oncogene?.Cancer Cell,2004,5:301-302.
13 Rahman L,Voeller D,Rahman M,et al.Thymidylate synthase as an oncogene:A novel role for an essential DNA synthesis enzyme.Cancer Cell,2004,5:341-351.
14 Zhang Y,Venkatraj VS,Fischer SG,et al.Genomic Cloning and Chromosomal Assignment of theE2F Dimerization Partner TFDP Gene Family.Genomics,1997,39:95-98.
15 Yasui K,Okamoto H,Arii S,et al.Association of over-expressed TFDP1 with progression of hepatocellular carcinomas.J Hum Genet,2003,48:609-613.
16 Saxena UH,Powell CM,Fecko JK,et al.Phosphorylation by Cyclin C/Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 2 following Mitogenic Stimulation of Murine Fibroblasts Inhibits Transcriptional Activity of LSF during G1 Progression.Mol Cell Biol,2009,29:2335-2345.
17 Schiffer CA,Clifton IJ,Davisson VJ,et al.Crystal structure of human thymidylate synthase:a structural mechanism for guiding substrates into the active site.Biochemistry,1995,34:16279-16287.
18 Dong S,Lester L,Johnson LF.Transcriptional control elements and complex initiation pattern of the TATA-less bidirectional human thymidylate synthase promoter.J Cell Biochem,2000,77:50-64.
19 Kim HR,Rahman FU,Kim KS,et al.Critical Roles of E2F3 in Growth and Musculo-skeletal Phenotype in Mice.Int J Med Sci,2019,16:1557-1563.
20 Reimer D,Sadr S,Wiedemair A,et al.Expression of the E2F family of transcription factors and its clinical relevance in ovarian cancer.Ann N Y Acad Sci,2007,1091:270-281.
21 He L,Yang H,MaY,et al.Identification of Aurora-A as a direct target of E2F3 during G2/M cell cycle progression.J Biol Chem,2016,291:22842.