近年来,在以患者为中心的大趋势背景下,由于专病化诊疗模式的局限性,多学科联合会诊(multidisciplinary team,MDT)已成为当今医学界广泛认可和推广的诊疗模式。特殊健康状态儿童是指存在基础疾病或疑似疫苗接种慎用征的儿童。鉴于部分特殊健康状态儿童所患基础疾病的多样性、复杂性,由此牵涉到多个学科,单独专科很难全面评估和把握病情。目前,鲜有MDT应用于特殊健康状态儿童免疫接种的报道。本研究通过收集MDT的特殊健康状态儿童病种、会诊专科、医学接种评估建议,并随访免疫接种后原发病转归及不良反应发生情况,旨在为特殊健康状态儿童免疫接种的多学科会诊管理模式提供参考,将医防融合落实于特殊健康状态儿童的免疫接种领域。
对象与方法
一、研究对象
以2021年1月至2022年5月,由广州市妇女儿童医疗中心特需人群接种门诊医学专家发起组织MDT的34例患儿为研究对象。满足以下条件:(1)存在基础疾病或疫苗接种慎用情况的特殊健康状态儿童,包括①基础疾病涉及2个及以上专科的患儿;②病情涉及多系统、多器官需要多个专科联合评估的患儿。(2)无法在社区预防服务中心免疫接种。(3)存在疫苗接种延迟。(4)有免疫接种需求。
二、多学科联合会诊工作流程
1.组建MDT评估专家组:集儿童保健科、免疫科、遗传代谢与内分泌科、感染科、血液科、心脏内科、神经内科、外科等临床科室专家,组建中心内的免疫接种评估MDT专家队伍。会诊专家要求具有副主任医师及以上职称,通过广州市预防医学会培训并考试合格,开通MDT权限并具备MDT资质。
2.会诊前准备:特需人群接种门诊专家提出MDT,征求家长意见,填写“院内疑难病例多学科会诊知情同意书”。登记医生整理相关资料,建立特殊健康状态儿童多学科会诊登记簿,详细记录患儿基本信息、病史、辅助检查、初步诊断、目前治疗等,填写会诊申请单,并通知MDT专家进行联合会诊,告知家长会诊时间。
3.会诊时要求:申请会诊的医生在会诊时报告病历,提出会诊目的,家长参与补充患儿相关资料和情况,详细体格检查,多学科专家参照传染性疾病罹患风险和疾病负担、免疫接种的安全性和有效性集中讨论,会诊组出具医学疫苗接种评估单,并向家长解释免疫接种具体实施方案。
4.会诊后随访管理:特需人群接种门诊设立安全观察随访表,追踪随访患儿的免疫接种、接种后不良反应发生情况,以及原发病的转归,并提出医学指导建议。
5.统计学处理:数据录入采用EPI data 3.1软件,使用SPSS 13.0统计软件分析。
结 果
一、一般资料
MDT患儿中男童占52.9%(18/34),女童47.1%(16/34)。主要为1岁以内婴儿和4~6岁儿童,均占32.4%(11/34),其次为1~3岁幼儿,所占比例为29.4%(10/34),7岁及以上所占比例最少,为5.9%(2/34)。
二、病种和疾病诊断分布
MDT会诊患儿中11.8%(4/34)有手术干预治疗病史,88.2%(30/34)为内科疾病。患儿有2种疾病诊断的所占比例最高,为44.1%(15/34),其次是3种、4种疾病诊断,分别为26.5%(9/34)、17.6%(6/34),5种及以上疾病诊断仅占8.8%(3/34)。其中41.2%(14/34)存在染色体异常或基因突变。
三、会诊专科情况
特需人群接种门诊主任医师发起并主持34次MDT,应邀参与会诊的涉及13个临床专科,会诊专家共111人次,参与率为100%。参与会诊次数最多的科室为神经内科,所占比例为28.6%(22/77),其次为免疫科(26.0%,20/77)、遗传代谢与内分泌科(22.1%,17/77)。
3个临床专科联合会诊所占比例最高,为64.7%(22/34),2个、4个临床专科共同会诊的均占14.7%(5/34),5个专科共同参与的占5.9%(2/34)。
四、医学接种评估建议
MDT会诊后79.4%(27/34)可以实施免疫接种,其中47.1%(16/34)可以按免疫规划程序接种疫苗,有1例垂体柄阻断综合征患儿应用氢化可的松、左甲状腺素钠、生长激素替代治疗,MDT会诊建议增加:原发病无免疫接种禁忌证,需注意接种后应激反应不足可能导致肾上腺皮质功能减退症危象,免疫接种后注意患儿应激反应情况,必要时需要增加氢化可的松剂量至替代剂量的2~5倍。32.4%(11/34)接种部分疫苗(见表1),其中72.7%(8/11)按免疫程序种非活疫苗。20.6%(7/34)暂缓免疫接种,5例以发育落后为主要表现,其中3例基因异常,分别为1例广泛性发育障碍、头颅MR见活动性改变,染色体[46,X,inv(Y)(p11.1q11.22)]、基因(SPECC1L)杂合突变患儿;1例脑白质病(LAMA2基因杂合变异)患儿,建议完善肌电图、神经传导速度检查,动态复查MRI排除脱髓鞘病变;1例染色体异常[46,XY,der(5)t(5;7)(q35.3;q32)mat]患儿;其中1例多发性动静脉瘘介入治疗术后(左下肢Park-Weber综合征)患儿,建议复查颅脑磁共振(既往提示脑室旁脑白质软化,双侧额叶改变,不排除脑发育不良),排除神经系统无进展性疾病如脱髓鞘、代谢性等病因;其中1例诊断不明,表现为疾病时运动倒退,病后可较快恢复,颅脑磁共振双侧额顶叶白质异常信号,双侧内叶皮质下白质、侧脑室室管膜下多发囊肿,建议完善GM1、GM2、Krabb等脑白质病变相关酶学检查。1例视网膜母细胞瘤结束化疗2月患儿,1例异基因造血干细胞移植(幼年型粒—单核细胞白血病)3月患儿。37.04%(10/34)推荐接种灭活流感疫苗和肺炎球菌疫苗,其中6例存在心肺基础疾病(2例慢性肺部疾病,1例膈疝术后,1例非结核分支杆菌感染,2例心脏疾患),1例肝脏移植术后,1例脊髓性肌萎缩症,1例人工耳蜗植入术后,1例慢性肾衰竭透析状态。
表1 接种部分疫苗患儿疾病诊断与医学评估建议对照表
Table 1 Comparison table of disease diagnosis and medical evaluation recommendations for children vaccinated with partial vaccines
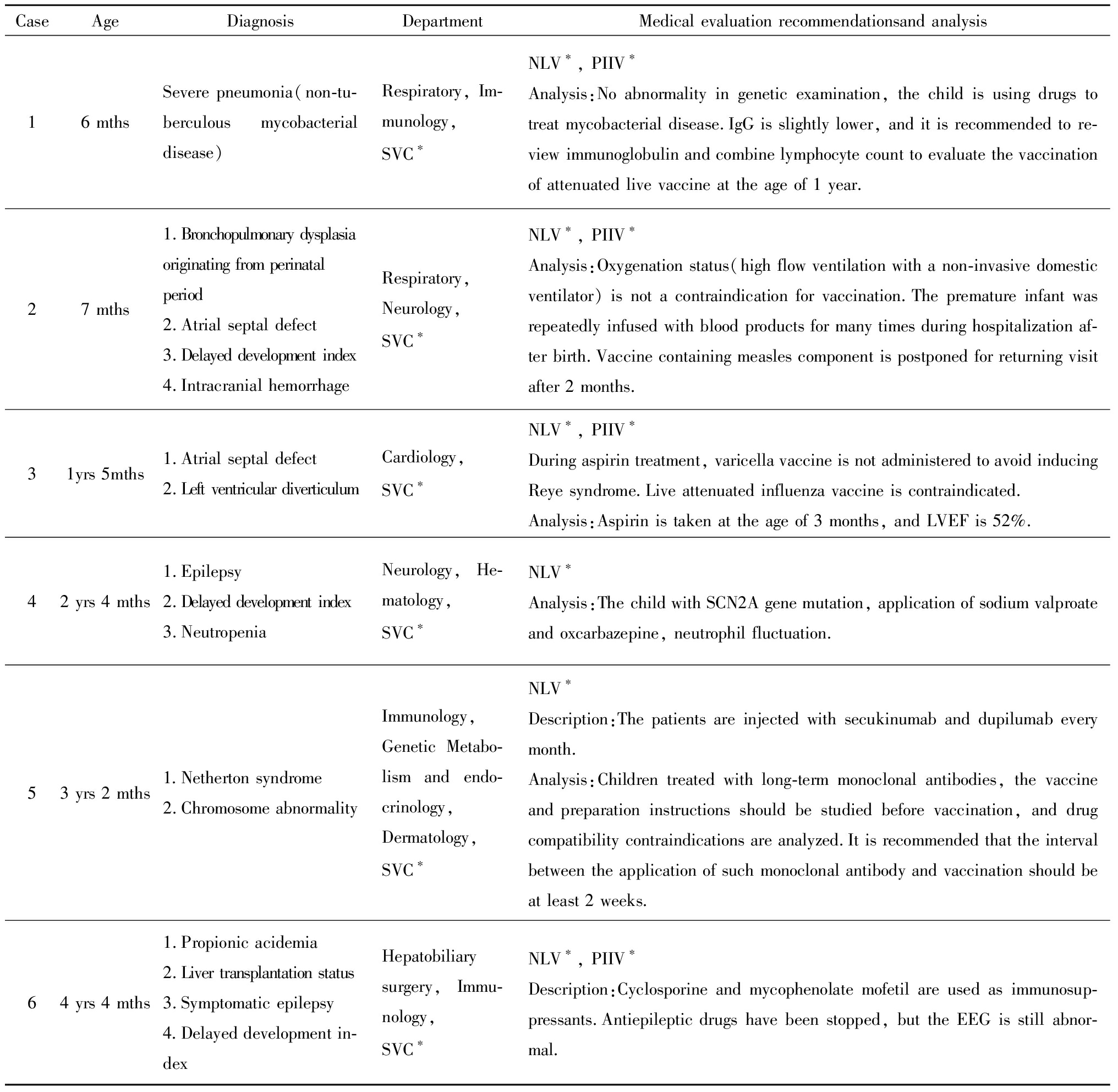
CaseAgeDiagnosisDepartmentMedical evaluation recommendationsand analysis16 mthsSevere pneumonia(non-tu-berculous mycobacterial disease)Respiratory, Im-munology,SVC∗NLV∗, PIIV∗Analysis:No abnormality in genetic examination, the child is using drugs to treat mycobacterial disease.IgG is slightly lower, and it is recommended to re-view immunoglobulin and combine lymphocyte count to evaluate the vaccination of attenuated live vaccine at the age of 1 year.27 mths1.Bronchopulmonary dysplasiaoriginating from perinatal period2.Atrial septal defect3.Delayed development index4.Intracranial hemorrhageRespiratory,Neurology,SVC∗NLV∗, PIIV∗Analysis:Oxygenation status(high flow ventilation with a non-invasive domestic ventilator) is not a contraindication for vaccination.The premature infant was repeatedly infused with blood products for many times during hospitalization af-ter birth.Vaccine containing measles component is postponed for returning visit after 2 months.31yrs 5mths1.Atrial septal defect2.Left ventricular diverticulumCardiology,SVC∗NLV∗, PIIV∗During aspirin treatment, varicella vaccine is not administered to avoid inducing Reye syndrome.Live attenuated influenza vaccine is contraindicated.Analysis:Aspirin is taken at the age of 3 months, and LVEF is 52%.42 yrs 4 mths1.Epilepsy2.Delayed development index3.NeutropeniaNeurology, He-matology,SVC∗NLV∗Analysis:The child with SCN2A gene mutation, application of sodium valproate and oxcarbazepine, neutrophil fluctuation.53 yrs 2 mths1.Netherton syndrome 2.Chromosome abnormalityImmunology,Genetic Metabo-lism and endo-crinology,Dermatology,SVC∗NLV∗Description:The patients are injected with secukinumab and dupilumab every month.Analysis:Children treated with long-term monoclonal antibodies, the vaccine and preparation instructions should be studied before vaccination, and drug compatibility contraindications are analyzed.It is recommended that the interval between the application of such monoclonal antibody and vaccination should be at least 2 weeks.64 yrs 4 mths1.Propionic acidemia2.Liver transplantation status3.Symptomatic epilepsy4.Delayed development in-dexHepatobiliary surgery, Immu-nology,SVC∗NLV∗, PIIV∗Description:Cyclosporine and mycophenolate mofetil are used as immunosup-pressants.Antiepileptic drugs have been stopped, but the EEG is still abnor-mal.
表1(续)
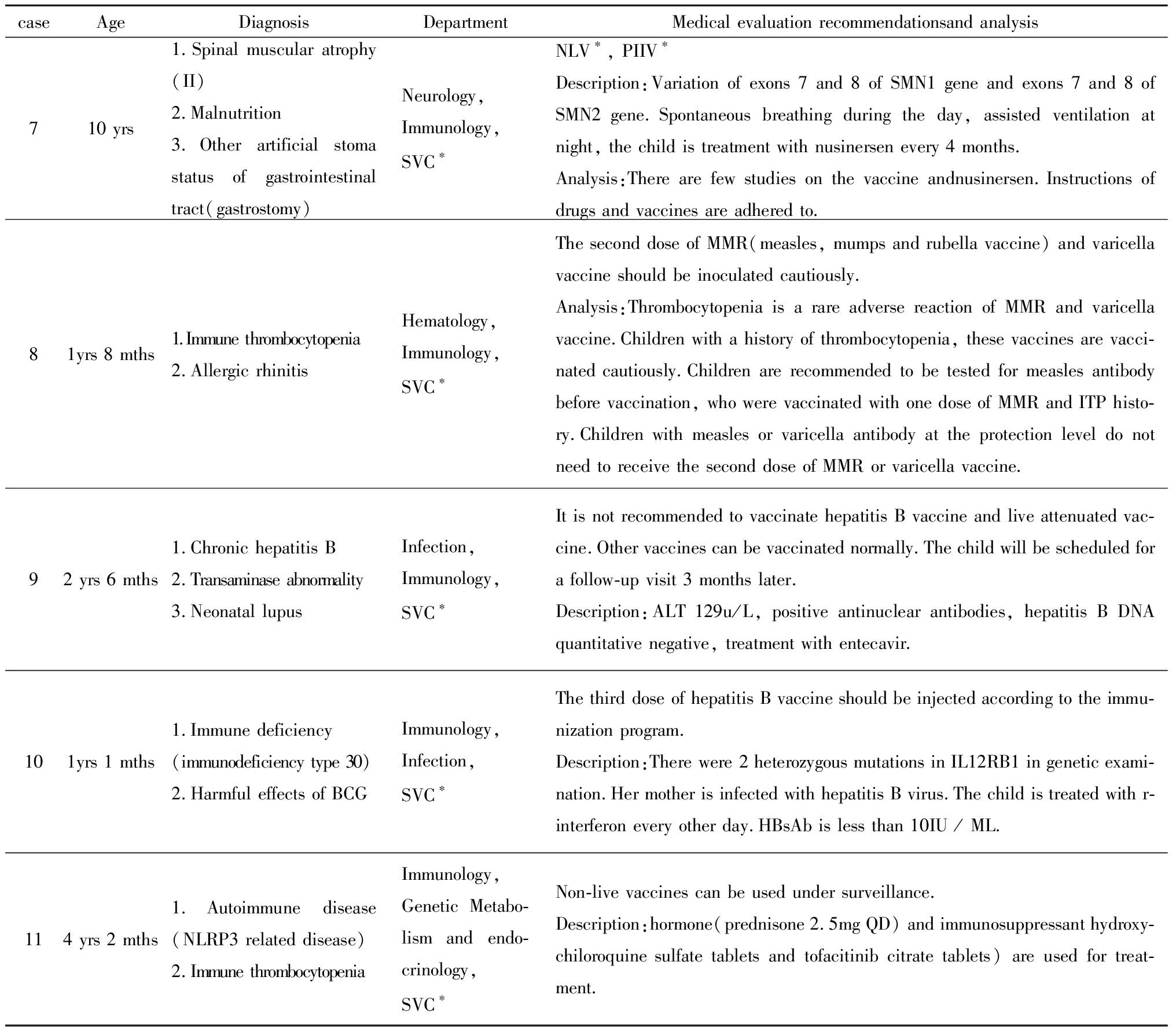
caseAgeDiagnosisDepartmentMedical evaluation recommendationsand analysis710 yrs1.Spinal muscular atrophy(II)2.Malnutrition3.Other artificial stoma status of gastrointestinal tract(gastrostomy)Neurology,Immunology,SVC∗NLV∗, PIIV∗Description:Variation of exons 7 and 8 of SMN1 gene and exons 7 and 8 of SMN2 gene.Spontaneous breathing during the day, assisted ventilation at night, the child is treatment with nusinersen every 4 months.Analysis:There are few studies on the vaccine andnusinersen.Instructions of drugs and vaccines are adhered to.81yrs 8 mths1.Immune thrombocytopenia2.Allergic rhinitisHematology, Immunology,SVC∗The second dose of MMR(measles, mumps and rubella vaccine) and varicella vaccine should be inoculated cautiously.Analysis:Thrombocytopenia is a rare adverse reaction of MMR and varicella vaccine.Children with a history of thrombocytopenia, these vaccines are vacci-nated cautiously.Children are recommended to be tested for measles antibody before vaccination, who were vaccinated with one dose of MMR and ITP histo-ry.Children with measles or varicella antibody at the protection level do not need to receive the second dose of MMR or varicella vaccine.92 yrs 6 mths1.Chronic hepatitis B2.Transaminase abnormality3.Neonatal lupusInfection,Immunology,SVC∗It is not recommended to vaccinate hepatitis B vaccine and live attenuated vac-cine.Other vaccines can be vaccinated normally.The child will be scheduled for a follow-up visit 3 months later.Description:ALT 129u/L, positive antinuclear antibodies, hepatitis B DNA quantitative negative, treatment with entecavir.101yrs 1 mths1.Immune deficiency(immunodeficiency type 30)2.Harmful effects of BCGImmunology,Infection,SVC∗The third dose of hepatitis B vaccine should be injected according to the immu-nization program.Description:There were 2 heterozygous mutations in IL12RB1 in genetic exami-nation.Her mother is infected with hepatitis B virus.The child is treated with r-interferon every other day.HBsAb is less than 10IU / ML.114 yrs 2 mths1.Autoimmune disease(NLRP3 related disease)2.Immune thrombocytopeniaImmunology,Genetic Metabo-lism and endo-crinology,SVC∗Non-live vaccines can be used under surveillance.Description:hormone(prednisone 2.5mg QD) and immunosuppressant hydroxy-chiloroquine sulfate tablets and tofacitinib citrate tablets) are used for treat-ment.
*NLV here refers to non-live vaccines are carried out according to the immunization procedure; PIIV here refers to pneumococcal and inactivated influenza vaccines are recommended;SVC here refers to special vaccination clinic.
五、免疫接种和接种后随访
34例患儿MDT前累计接种疫苗171剂次,平均5剂次/人,MDT后累计接种255剂次,平均12剂次/人(见表2)。接种后24 h、5 d、15 d、42 d、3 mths由随访专员根据安全观察随访表内容(基础疾病、接种疫苗名称、接种后是否发生不良反应、是否按疑似预防接种异常反应上报、不良反应变化情况以及基础疾病转归)进行随访,累计1 275次,有1例待移植慢性肾衰竭透析状态患儿接种麻腮风联合减毒活疫苗当天出现高热(热峰39.0℃,为全身不良反应),本例以疑似预防接种异常反应个案上报中国疾病预防控制信息系统,经降低透析液温度后患儿热可退,系一般不良反应,一般不良反应发生率为0.4%(1/255),无异常反应。100%(27/27)免疫接种后监测基础疾病稳定。
表2 MDT患儿免疫接种率与不良反应发生率
Table 2 Immunization rate and incidence of adverse reactions in children with MDT
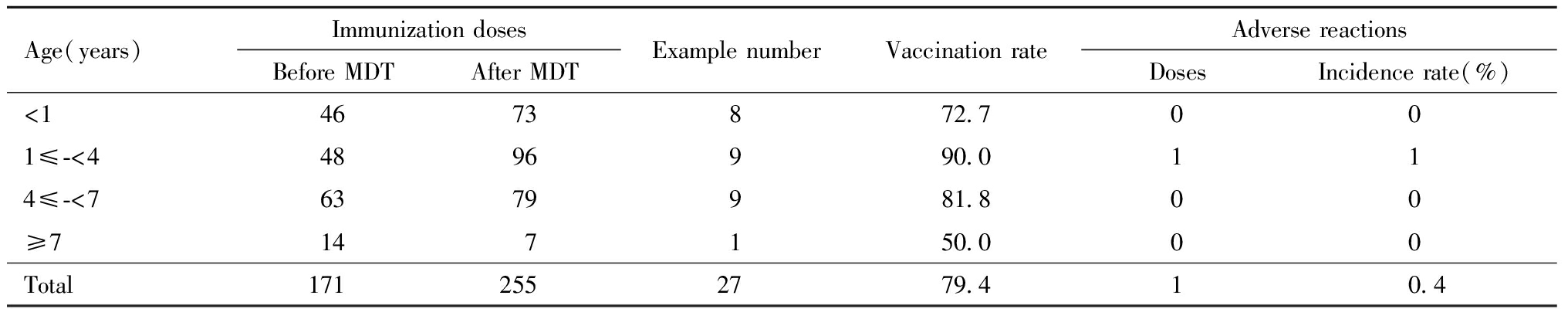
Age(years)Immunization dosesBefore MDTAfter MDTExample number Vaccination rateAdverse reactionsDosesIncidence rate(%)<14673872.7001≤-<44896990.0114≤-<76379981.800≥7147150.000Total1712552779.410.4
讨 论
特殊健康状态儿童较普通儿童更易遭受感染[1],通常这类儿童在疫苗接种中属于慎种人群。国内对于特殊健康状态儿童的免疫接种尚处于探索阶段,研究表明特殊健康状态儿童免疫接种率低,疫苗接种延迟明显[2]。不同的健康状态不能简单地用单一体征或宽泛性描述一概而论,应该针对不同的情况进行具体分析并及时采取免疫接种措施进行保护。
MDT形成于20世纪60年代,其核心理念是以患者为中心[3],涉及多系统多器官疾病时,由不同学科专家共同参与,为患者提供最佳的综合诊疗方案,有利于集中优势资源,保障医疗安全,同时促进学科间的交流与协作[4]。MDT多用于临床疾病的诊治,鲜有应用于免疫接种的文献报道。针对特殊健康状态儿童免疫接种,近年来,国内专家制定了一些共识,包括2014年免疫异常儿童疫苗接种(上海)专家共识[5]、中华医学会儿科学分会免疫学组联合《中华儿科杂志》编辑委员会2015年提出的“免疫功能异常患儿的预防接种专家共识(试行稿)” [6]、2018年特殊健康状态儿童预防接种(上海、苏州、杭州)专家共识[7]以及2020年特殊状态儿童预防接种(广东)专家共识[8]。这些共识是在既有原则下,从循证医学角度出发,汇总专家们的意见,对特殊健康状态儿童的疫苗接种问题进行分析、利弊评价,并提出解决方案或建议。然而,往往是针对一类特殊健康状态,对于基础疾病同时涉及多个专科的复杂情况,可以通过多学科平台,采用“多对一”的诊查模式,显著缩短转诊至各个专科评估的时间,避免了医师个人的主观片面性,经相关领域专家讨论,增加了评估的准确性,结合各专家意见制定个体化的免疫接种方案,使及时免疫接种/补种成为可能。通过专家介绍免疫接种计划,从专业角度解释该患儿对疫苗可预防疾病的易感性、罹患疫苗可预防疾病的健康危害,从专科角度分析免疫接种后基础疾病可能的转归方向、接种后不良反应发生情况等,实现同家长信息共享,有助于增强他们对于特殊群体免疫接种的信心。本研究通过对34例复杂疾病的特殊健康状态儿童组织MDT,为79.4%(27/34)患儿提供免疫接种方案,100%(27/27)按MDT医学评估接种建议执行,免疫接种依从性好。
MDT模式管理要求建立严密的随访制度,实现全流程的闭环管理。对于特殊健康状态儿童,疫苗接种的安全性尤为重要,通过主动及被动监测不良反应和基础疾病的转归,实现对这类儿童的精细化管理和指导。本研究通过对27例特殊健康状态儿童免疫接种后随访管理,所有患儿基础疾病均稳定,一般不良反应发生率为0.4%(1/255),提示这类儿童免疫接种有较好的安全性。
通过MDT在特殊健康状态儿童免疫接种中的应用,整合了多学科会诊的医学专家,提出了科学的医学接种评估建议,制定了最合适特殊健康状态儿童的个性化接种方案,提高了疫苗接种率及对可预防疾病的防控水平。
1 Lehman H,Hernandez-Trujillo V,Ballow M.Diagnosing primary immunodeficiency:a practical approach for the non-immunologist.Curr Med Res Opin,2015,31:697-706.
2 韩英,胡丹丹,韦茹,等.广东省特需人群接种门诊特殊健康状态儿童预防接种探索.中国疫苗和免疫,2021,27:678-683.
3 Bannon SA,Mork M,Vilar E,et al.Patient-reported disease knowledge and educational needs in Lynch syndrome:findings of an interactive multidisciplinary patient conference.Hered Cancer Clin Pract,2014,12:1.
4 何晶波,栾瑞,潘宇,等.我院临床多学科联合会诊情况分析.中国医院管理,2015,35:34.
5 上海市医学会儿科专业委员会免疫学组,上海市免疫学会儿科临床免疫专业委员会,上海市预防医学会免疫规划专业委员会.免疫异常儿童疫苗接种(上海)专家共识.临床儿科杂志,2014,32:1181-1190.
6 中华医学会儿科学分会免疫学组.免疫功能异常患儿的预防接种专家共识(试行稿):原发性免疫缺陷病.中华儿科杂志,2015,53:898-902.
7 苏州市疾病预防控制中心,上海市疾病预防控制中心,杭州市疾病预防控制中心,等.特殊健康状态儿童预防接种专家共识之十七——白血病化疗与预防接种.中国实用儿科杂志,2019,34:266-267.
8 广东省医师协会儿科医师分会.特殊状态儿童预防接种(广东)专家共识.中华实用儿科临床杂志,2020,35:401-410.